


Tel:189-1186-2450
Mobile:189-1186-2450
Email:njzzcg888@163.com
Address:7th Floor, R&D Building, Building 51, Emerging Industries, Nanjing University Science Park, No. 8 Yuanhua Road, Xianlin Street, Qixia District, Nanjing City; Beijing Office: No.1 Zhongliang Road, Daxing District, Beijing, Zhuzong Vanke Plaza
Source:Quasi intelligent sensing Time:2024-06-27
1. Overview
With the increase in electricity consumption in cities and factories, the level of automation has correspondingly improved, and the amount of cables used is increasing. Due to the increase in wire length, the probability of fire accidents also increases accordingly. At present, most power supply systems under construction and operation still use flammable cables, so the issue of cable fire prevention is particularly prominent.
According to the analysis of power accidents, fires caused by cable faults will lead to extensive cable burning, resulting in forced shutdown and inability to resume production in a short period of time, causing significant economic losses. Through the analysis of the accident, the direct cause of the fire in the cable trench is poor quality of the middle end of the cable, loose compression joints, and excessive contact resistance. Long term operation causes the cable head to overheat and burn through the insulation, ultimately leading to the occurrence of a fire in the cable trench. We have designed this power cable fire warning system based on the above analysis.
Overheating faults in electrical equipment can be divided into two categories: external thermal faults and internal thermal faults:
1)、External thermal failure
The external thermal failure of electrical equipment mainly refers to the hidden danger caused by the temperature increase and contact resistance increase of exposed joints due to poor crimping and other reasons under the action of high current, resulting in a vicious cycle. This type of fault accounts for a significant proportion of external thermal faults90%above. According to data statistics, it can be seen that thermal faults of wire clamps and knife switch contacts account for a significant proportion of external thermal faults77%,Their average temperature rise is about30The average temperature rise of other external joints is around degrees Celsius20-25Based on testing experience and temperature rise, external faults can be classified into three types: mild, moderate, and severe.
2)、Internal thermal failure
The characteristic of internal thermal faults in high-voltage electrical equipment is that the fault point is sealed in insulation materials or metal shells, such as cables. Internal thermal faults generally have a long and stable heating time, and heat transfer occurs with the surrounding conductors or insulation materials, causing local temperature rise. Therefore, internal faults in high-voltage electrical equipment (such as cables) can be diagnosed by detecting the temperature rise of the surrounding materials.
2、Introduction to Distributed Fiber Optic Temperature Measurement SystemDistributed fiber optic sensing technology is currently the most advanced sensing technology internationally, and its principle is mainly based on Raman scattering of light in optical fibers Scattering effect. When a light pulse is emitted from one end of the fiber into the fiber, This optical pulse undergoes Raman scattering as it propagates forward along the fiber optic. The Raman scattering light reflected back from the optical fiber is decomposed into Stokes scattering light and Antitokes scattering light of different wavelengths through a spectral separation module. The intensity of Stokes scattered light is weakly correlated with temperature; The intensity of Antitokes scattered light is strongly correlated with temperature; By processing and comparing the two optical signals, the temperature distribution curve along the fiber is obtained& nbsp; The distributed fiber optic sensing system utilizes optical time-domain reflection (OTDR) technology to locate all temperature points by calculating the transmission speed and echo time of light waves.
The advantages of distributed fiber optic temperature detection technology include:
1)Distributed measurement: can continuously determine the temperature distribution along the fiber optic cable, without temperature blind spots;
2)Long distance detection: detection technology with a maximum length of 10km for a single channel;
3)High positioning accuracy: ± 0.5 meters (10km/channel));± 0.05 meters (3km/channel);
4)Multiple monitoring channels: A single host can support up to 16 channels;
5)Intrinsic lightning protection: Lightning often damages a large number of electrical sensors, and the impact of lightning on highway tunnels is particularly severe. The temperature sensing fiber optic is completely electrically insulated and can withstand the impact of high voltage and high current。
6) Anti electromagnetic interference: Fiber optic temperature detection, belonging to non electric detection technology, has good anti electromagnetic interference ability;
7)Simple structure: The entire sensing system consists of two parts: a fiber optic temperature measurement host and a temperature sensing optical cable. The structure is simple and the construction partyConvenient, easy to maintain。
3、Composition of temperature measurement systemThe distributed fiber optic temperature measurement system consists of a distributed fiber optic temperature measurement host, temperature sensing fiber optic, cabinet (optional), industrial control computer (optional), platform monitoring software (optional), etc。

Host technical performance(ZZ-DTS) | |
Fiber type | Multimode fiber62.5/125&50/125,Single-mode optical fiber9/125Customizable |
Product Architecture | The device adopts embedded technologyFPGA+ARMDesign, independent of operating system, adaptable to any operating system. All internal circuits of the machines are treated with three protections, including moisture-proof, leakage proof, dust-proof, corrosion-proof, anti-aging, and corona resistant *Internal integration of the hostWindowsLocal display on industrial computer (optional) |
Measure distance | 10km(Standard configuration), optional15km、20kmSpecifications |
Data sampling rate | 200Mbps,Optional250Mbps |
spatial resolution | 0.5-3m(sampling rate0.4Rice or0.5rice) |
positioning accuracy | ±0.5m-±1m |
Positioning resolution | ±0.5mperhaps±0.4m |
Measurement time | ≤0.5s/km,Typical value3S/passageway(10kmwithin) |
Temperature measurement range | -40℃-700℃(depending on fiber optic cable) |
Temperature measurement accuracy | ±0.5℃@3km,±1℃@6km, ±1.5℃@10km |
Temperature resolution | 0.01℃ |
Measurement channel | ≤16 |
Fiber optic connectors | FC/APC |
Working power supply | 9-36VWide DC voltage, average power consumption≤8W,Standard power supply:24VDC |
Operating temperature | -10℃-60℃ |
Storage temperature | -20℃-70℃ |
External display | ( Optional configuration)4.3An inch LCD screen that displays temperature curves, temperature measurement cable construction quality, network configuration, equipment self inspection, equipment information display, alarm recording, alarm threshold setting, equipment noise reduction and other functional units to the outside world |
communication interface | 1roadRJ45Ethernet,supportTCPagreement; 1roadRS232(Auxiliary data communication, external serial port to network port module, and main communication port form independent dual network ports, supportingTCPagreement,ModbusRTUagreement); 2roadRS485(supportModbusRTUProtocol module、64Extension of circuit relays, docking with fire alarms and other protocol modules); 8Road relay (equipment built-in, can connect with fault alarm and temperature fire alarm); |
Dimensions (length, width, height) | 482.6mm×458.4mm×89mm |
weight | 8KG |
4、Temperature monitoring and laying plan for high-voltage cables
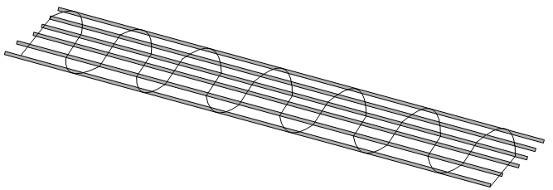
1Cables: Especially high-voltage cables are the focus of monitoring, and temperature sensing optical cables are used along the cable layerSType laying:
Ø Outdoor pipe gallery bridge
Ø Cable trench in distribution room
Ø Cable interlayer in distribution room


 189-1186-2450
189-1186-2450
 7th Floor, R&D Building, Building 51, Emerging Industries, Nanjing University Science Park, No. 8 Yuanhua Road, Xianlin Street, Qixia District, Nanjing City; Beijing Office: No.1 Zhongliang Road, Daxing District, Beijing, Zhuzong Vanke Plaza
7th Floor, R&D Building, Building 51, Emerging Industries, Nanjing University Science Park, No. 8 Yuanhua Road, Xianlin Street, Qixia District, Nanjing City; Beijing Office: No.1 Zhongliang Road, Daxing District, Beijing, Zhuzong Vanke Plaza
Copyright© All Rights Reserved for Intelligent Sensing SuICPB No. 2024111040 技术支持:中企云达